Backing up and recovering from disasters is crucial for maintaining your WordPress site.
A backup is like a safety net, a copy of all your website’s stuff so you can bring it back if something goes wrong.
Disaster recovery is about planning to get your site back on track after a major mess-up. Both of these are key for keeping your data safe and your site up and running smoothly.
Data is the lifeblood of businesses and individuals alike, and protecting that data against loss or corruption is essential. This is where data backup and disaster recovery come into play. Imagine your computer crashing or a natural disaster compromising your entire data center.
How would you recover your precious files, documents, and databases? That’s where understanding data backup and disaster recovery becomes essential.
Contents
- Who can Benefit from Data Backup?
- Types of Data Backup
- Components of Disaster Recovery
- Local vs. Cloud Backup Solutions
- Difference Between Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Backup vs. Disaster Recovery
- Best Practices for Data Backup
- Are You Ready to Enable Automatic Backups with WP Staging Pro?
- Conclusion
- Related Articles
Who can Benefit from Data Backup?
Data backup involves making duplicate copies of your data to ensure its safety if the original data is lost, damaged, or hacked.
On the other hand, disaster recovery is all about getting everything back in order after a major disaster, whether natural or caused by humans.
Think of a backup as a safety net for your website—it’s there to restore everything if something bad happens, like a cyber-attack or hardware failure.
Disaster recovery is like the playbook for getting things back on track quickly so your website can keep running smoothly without too much interruption.
Data has become the cornerstone of modern businesses. From customer information to financial records, organizations rely heavily on data for decision-making and operations.
Thus, ensuring the integrity and availability of this data is essential. Data backup is a safety net, offering peace of mind and knowing that critical information remains intact despite adversity.
Types of Data Backup
Data in WordPress can be backed up in various ways, each with its pros and cons. There are full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups.
Full backups cover everything, while incremental and differential backups only save what’s changed since the last backup.
They are quicker and take up less space, but they might make restoring a bit trickier.
1. Manual Backups
A manual backup is like making a physical copy of a site, just in case something happens to the original.
You’re taking matters into your own hands by creating copies of all your website’s files and database (think of that as the information behind the website).
While this gives you complete control, it’s essential to know that making manual backups can be time-consuming and requires some technical knowledge to do it properly.
2. Automated Backups
Remember a significant birthday? Automated backups are like having a trusty friend who remembers to back up your website for you, even when you’re busy.
Instead of depending on yourself to create copies (which can be irritating), you can use plugins or services offered by your web hosting company.
These tools work in the background, automatically backing up your website regularly, saving you time and effort. It is especially helpful if you prefer a more hands-off approach to website maintenance.
Emphasize ease of use with the “WP Staging” plugin, highlighting its simplicity in setting up automated backups, potentially mentioning “without any technical knowledge” or “in just a few clicks.”
Cloud Backups
Cloud backups are like storing those data in a secure online vault, separate from your home. This adds an extra layer of protection if anything happens at your place.
Plus, with cloud backups, you can access your data from any device with an internet connection anytime you need it. It’s like having your photos readily available, no matter where you are.
Components of Disaster Recovery
A comprehensive disaster recovery plan comprises several key components, including:
- Risk Assessment – Identifying potential threats and vulnerabilities to data and systems.
- Backup Strategies – Establishing protocols for regular data backups to minimize data loss.
- Emergency Response – Outlining procedures for responding to and mitigating the impact of disasters.
- System Recovery – Detailing steps for restoring hardware, software, and data to operational status.
- Testing and Training – Conduct regular tests and training exercises to ensure emergency readiness.
Local vs. Cloud Backup Solutions
– Local Backup
Local backup means keeping your backup data on servers or devices in your office or data center.
It gives you direct control over where your data is and lets you get to it fast. But there’s a downside: if something terrible happens to your office, like a fire or flood, your backup could be at risk too
– Cloud Backup
Alternatively, you can opt for cloud backup solutions, where your data is stored remotely in a cloud storage service or a third-party data center.
Cloud backup offers multiple advantages over traditional on-premises backup methods. These include:
- Scalability: Cloud backup services typically offer scalable storage options, allowing you to easily adjust your storage capacity as your data needs change over time.
- Redundancy: Cloud backup solutions often incorporate redundancy measures to ensure data integrity and availability. Your data may be replicated across multiple servers or data centers, reducing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or other issues.
- Accessibility: Cloud backup enables you to access your data from anywhere with an internet connection, providing greater flexibility and convenience compared to local backup solutions that may require physical access to storage devices.
- Off-site Protection: By storing data off-site in a secure cloud environment, you gain protection against localized disasters that could impact your primary data center or office location.
- Automation and Ease of Management: Many cloud backup services offer automated backup schedules and management features, simplifying data backup and management.
Difference Between Backup and Disaster Recovery
While data backup and disaster recovery are closely related, they serve distinct purposes.
Data backup primarily focuses on creating copies of data to protect against data loss, corruption, or accidental deletion.
Conversely, disaster recovery encompasses broader processes and procedures for restoring data, hardware, and software access after a disaster strikes.
Backup vs. Disaster Recovery
- Purpose: Data backup protects against data loss, while disaster recovery focuses on restoring operations after a disaster.
- Scope: Backup typically involves copying data, while disaster recovery encompasses broader processes for restoring systems and operations.
- Timeline: Backup can be performed regularly, while disaster recovery is activated in response to a disaster.
- Outcome: Backup ensures data availability, while disaster recovery aims to restore full operations.
Best Practices for Data Backup
While implementing a data backup strategy is essential, following best practices can enhance its effectiveness and reliability. Some critical best practices include:
1. Take Regular Backups
The top recommendation for backup and disaster recovery is to make website backups consistently.
It’s best to do this weekly or daily. By doing so, you’ll always have a recent backup ready to restore your website if needed, giving you peace of mind.
– Backing Up at Multiple Locations
Another effective strategy is to diversify where you store your backups. This includes keeping copies on your web server, an external hard drive, and in cloud storage.
Applying your backups across multiple locations reduces the risk of losing them if any storage location encounters issues.
- Backup from WordPress to Google Drive
- Backup from WordPress to Amazon S3
- Backup from WordPress to Dropbox
– Verifying Backups to Ensure Successful Restoration
Lastly, you must routinely test your backups to confirm their restoration capability. Download a backup copy and conduct tests to verify its usability for website restoration. This step guarantees your backups’ reliability and readiness for emergency use.
Are You Ready to Enable Automatic Backups with WP Staging Pro?
It might be time to consider enabling automatic backups with WP Staging Pro. This powerful plugin offers a range of features to simplify the backup process and provide peace of mind, knowing that your website’s data is secure.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to enabling automatic backups with WP Staging Pro:
Install WP Staging Pro:
- Install Plugin: Navigate to the menu on the left, click “Plugins,” and click “Add New.”
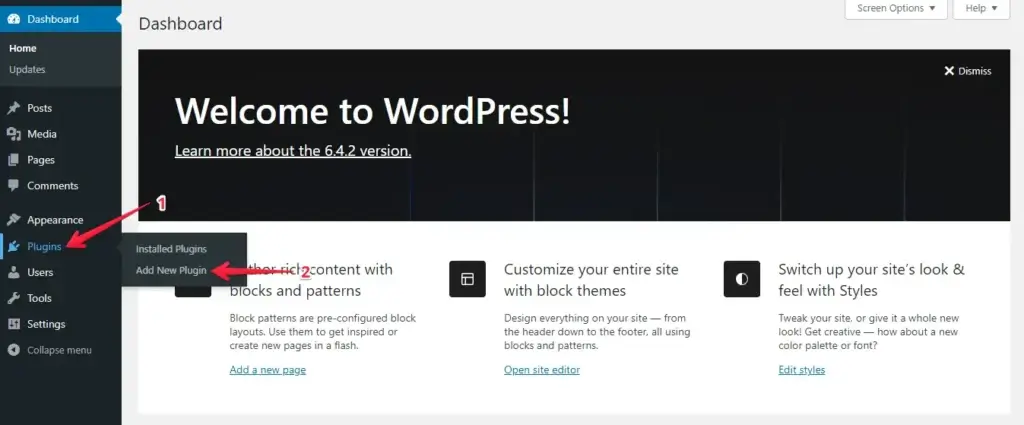
- Upload Plugin: Press the “Upload Plugin” button and click “Choose File” to upload the WP Staging Pro plugin.
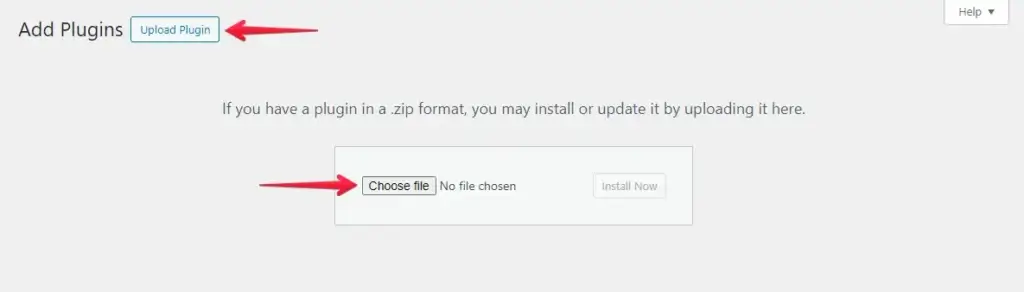
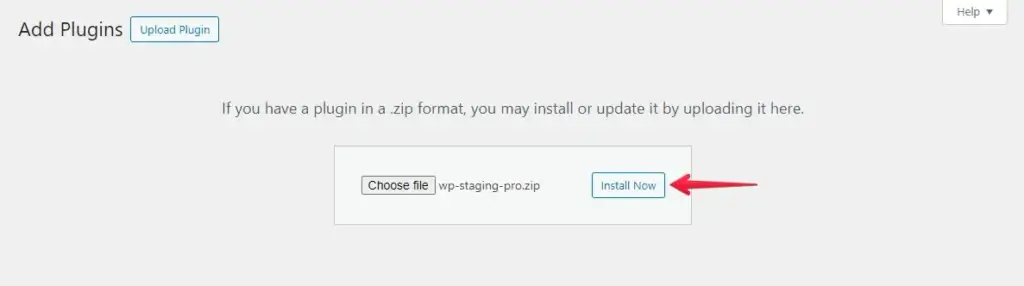
- Afterward, click the ‘Install Now’ button.
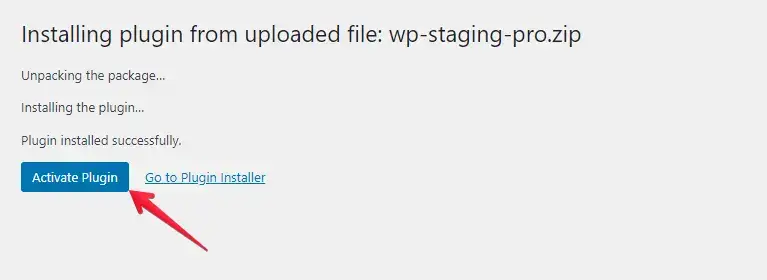
- After installing the plugin, proceed to activate it.
- Navigate to Backup Settings: Click the “Create Backup” button, but unselect the “One-Time-Only” checkbox.
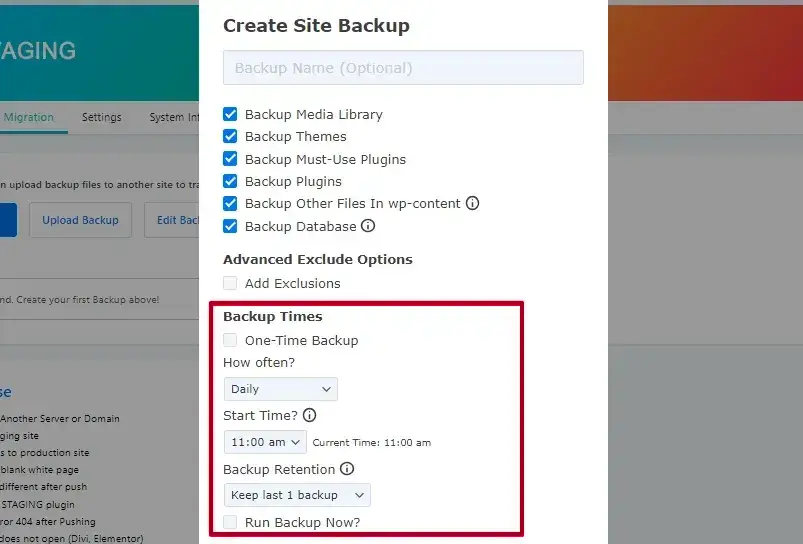
This image shows three options: “How often” to set the backup frequency (hourly, daily, weekly, etc.), “Start Time” to choose when backups begin, and “Backup Retention” to decide how many backups to keep.
Choose your preferred platform, click the active link, configure your account settings, and click “Start Backup” to begin the process.
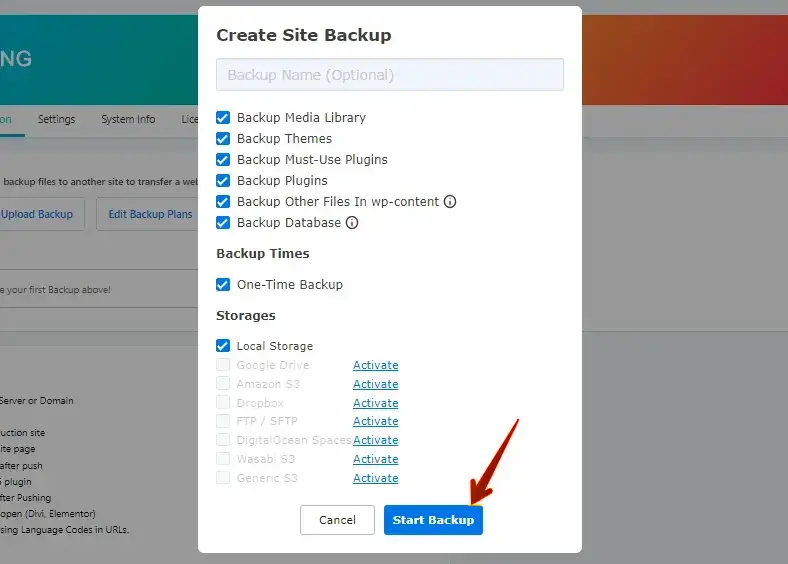
Double-check your backup schedule and settings to ensure that everything is configured correctly. You should see a confirmation message indicating that automatic backups have been enabled.
Conclusion
Securing your WordPress site with backups is essential. With a backup plan, you can avoid losing data and facing downtime. Regularly create, store, and test backups.

